Carbon neutrality/climate change action
Basic approach
Idemitsu Kosan is committed to fulfilling its "responsibility to support people's lives" and "Responsibility to protect the global environment now and in the future" by leveraging the strengths of its own group provide for society power to realize a carbon neutral (CN) and recycling-oriented society. With regard to climate change-related initiatives, we will continue to strengthen information disclosure in a manner consistent with the framework of the TCFD recommendations, which we signed in support of in 2020, and accelerate our efforts with the understanding and cooperation of all our stakeholders.
Signing of support for the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)

On February 14, 2020, we endorsed and signed the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD).
Climate change-related disclosures on this website
The pages on which each item of the TCFD framework is posted on this website are listed in the table below.
| Region | TCFD recommendations | Our disclosure |
|---|---|---|
| Governance | ① Explain the board of directors' monitoring system for climate-related risks and opportunities. | Governance |
| ② Explain the role of management in assessing and managing climate-related risks and opportunities. | ||
| Strategy | ① Describe the short-, medium-, and long-term climate-related risks and opportunities that the organization has identified. |
Officer message Strategy |
| ② Explain the impact of climate-related risks and opportunities on the organization's business strategy and financial planning. | ||
| ③ Explain the resilience of the organization's strategy based on considerations based on various climate-related scenarios, including the 2°C or lower scenario. | ||
| Risk management | ① Describe the process by which the organization identifies and assesses climate-related risks. | Risk management |
| ② Explain the process by which the organization manages climate-related risks. | ||
| ③ Describe how the organization's processes for identifying, assessing, and managing climate-related risks are integrated into the organization's overall risk management. | ||
| Metrics and targets | ① The organization discloses the metrics it uses to assess climate-related risks and opportunities in line with its own strategy and risk management processes. | Metrics and targets |
| ② Explain Scope 1, Scope 2, and if applicable to the organization, Scope 3 GHG emissions and related risks. | CO₂ emissions (Scope 1, 2, 3) actual trends | |
| ③ Disclose the goals the organization uses to manage climate-related risks and opportunities, and its performance against those goals. | Metrics and targets |
(Supplementary item)
| Region | TCFD recommendations | Our disclosure |
|---|---|---|
| Greenhouse gas emissions | Absolute emissions and emissions intensity for Scope 1, 2, and 3 | CO₂ emissions (Scope 1, 2, 3) actual trends |
| Transition | The amount and scope of assets or business activities vulnerable to transition risks; | Risks and opportunities |
| Physical risk | The amount and extent of assets or business activities vulnerable to physical risks; | Risks and opportunities |
| Climate-related opportunities | Proportion of revenue, assets and business activities linked to climate-related opportunities | Risks and opportunities |
| Capital deployment | Capital expenditures, financing and total amounts deployed towards climate-related risks and opportunities | Investment decision-making system |
| ICP | Price per ton of CO₂ emissions used within the organization (internal carbon price) | Investment decision-making system |
| Reward | Percentage of executive compensation linked to climate considerations | Executive compensation |
Governance
An overview of our corporate governance system is provided in the link below, and supplementary information regarding our response to climate change is provided below.
Board of directors
For our company, whose main business is the sale of fossil fuels, responding to climate change is one of our most important management issues, and it is an initiative that will involve a large-scale transformation of our business portfolio over the medium to long term.
The Board of Directors has the role of determining management policies based on a multifaceted approach to this issue, and supervising that actions based on those policies are carried out quickly and steadily.
The 11 directors who make up the Board of Directors are people with experience, track record, and knowledge in a variety of fields, including the environment, Resources circulation, domestic and international energy transition trends, related advanced technology, and sustainability.
Major climate change-related proposals are submitted to the Management Committee, which is the highest deliberative body for business execution, and particularly important matters are reported to the Board of Directors. This has created a system in which the Board of Directors supervises whether execution is steadily being carried out based on company-wide policies.
Business execution
Efforts to address climate change are company-wide and cover a wide range of themes. Therefore, we recognize the need to accelerate the planning and execution of company-wide strategies to realize a carbon-neutral (CN) society, and our specialized department (CNX * Strategy Office) is taking the lead in promoting this. Carbon Neutral Transformation Department leads company-wide CN strategy planning, GHG reduction target setting, and CNX human resource development in collaboration with related internal departments.
Each business division formulates and executes its own CN strategy based on company-wide policies. These major responses to climate change, led by each department within the company, are brought forward to the Executive Committee, where the content is deliberated in light of company-wide policies. The members of the Management Committee place emphasis on diversity in their specialized fields and areas of responsibility, and have established a system for comprehensive and effective discussions on cross-divisional issues and risks.
* CNX: Carbon Neutral Transformation
*1 Establishment of management policies based on climate change issues Supervising the implementation of actions based on policies
*2 Deliberation of major climate-related topics
*3 Scenario analysis, company-wide investment and loan policy formulation and management
*4 Company-wide CN strategy planning, GHG reduction target setting, progress monitoring of each department strategy
*5 GHG emissions capture and monitoring
*6 CN strategy planning and execution by business division
Linking climate change response and executive compensation
The remuneration system for our directors (excluding part-time directors and outside directors) and senior executive officers and above consists of ① fixed compensation, ② performance-linked bonuses, ③ performance-linked stock compensation, and ③ performance-linked stock compensation. It also includes CO₂ reduction indicators that are essential for realizing a carbon-neutral, recycling-oriented society.
Strategy
Scenario analysis
Long-term energy business environment scenario towards 2050
To specifically consider how to respond to climate change, we have formulated a long-term business environment scenario for the period up to 2050, identified risks and opportunities based on the output of the scenario, and are moving forward with the formulation of specific strategies.
Since the Company's first public announcement of its business environment scenario in 2019, the scenario has been reviewed from time to time in response to changes in the social environment, and three scenarios have been assumed when considering Medium-term Management Plan (FY2023-FY2025). Among these, we have formulated a plan with a strong awareness of the "Hekiten+" scenario, which is similar to the IEA's net zero scenario, which would make the most progress in decarbonization.
In the "Hekiten+" scenario, governments around the world take measures at a rapid pace to achieve the "1.5℃ target," and various decarbonization technologies are provide for society at an extremely rapid pace. We envision a world where this is achieved. In this scenario, in addition to renewable energy, various decarbonization technologies will be introduced, including nuclear power generation, hydrogen/ammonia combustion power generation, thermal power generation with CCS (Carbon Capture and Storage), synthetic fuel, and negative emissions. The goals of the Paris Agreement will be achieved through “total war.” Furthermore, oil demand in the Asia-Pacific region is expected to peak in 2025, and domestic oil demand is expected to decline by 30% in 2030, 60% in 2040, and 80% in 2050 compared to 2019. is.
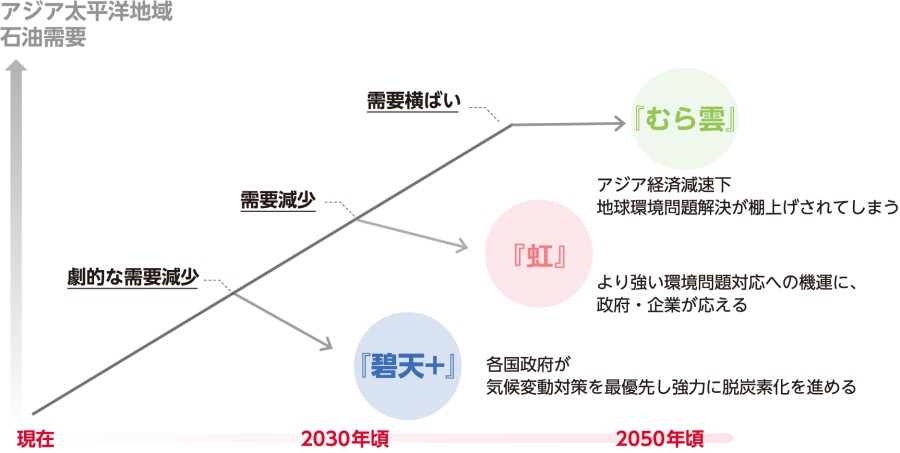


*The three business environment scenarios are unique to our company, but the following are scenarios from other organizations that are similar to each scenario.
Cloud: IEA Stated Policies Scenario
Rainbow: Between the IEA Stated Policies Scenario and the Sustainable Development Scenario
Hekiten+: IEA Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario
●Long-term energy demand outlook



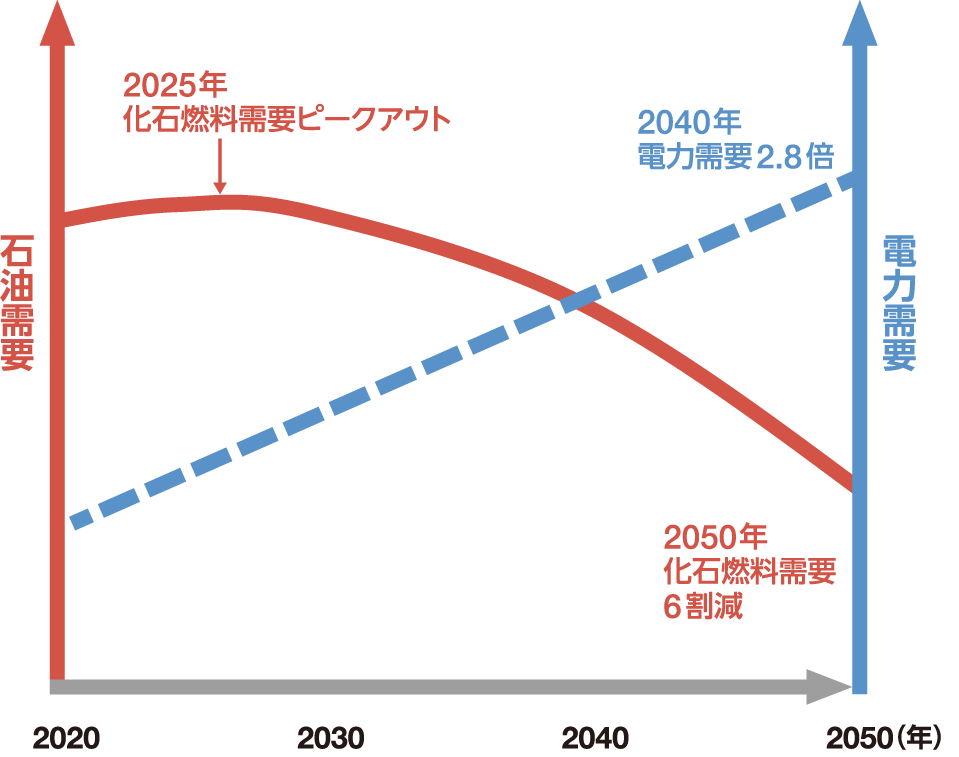
Asia Pacific
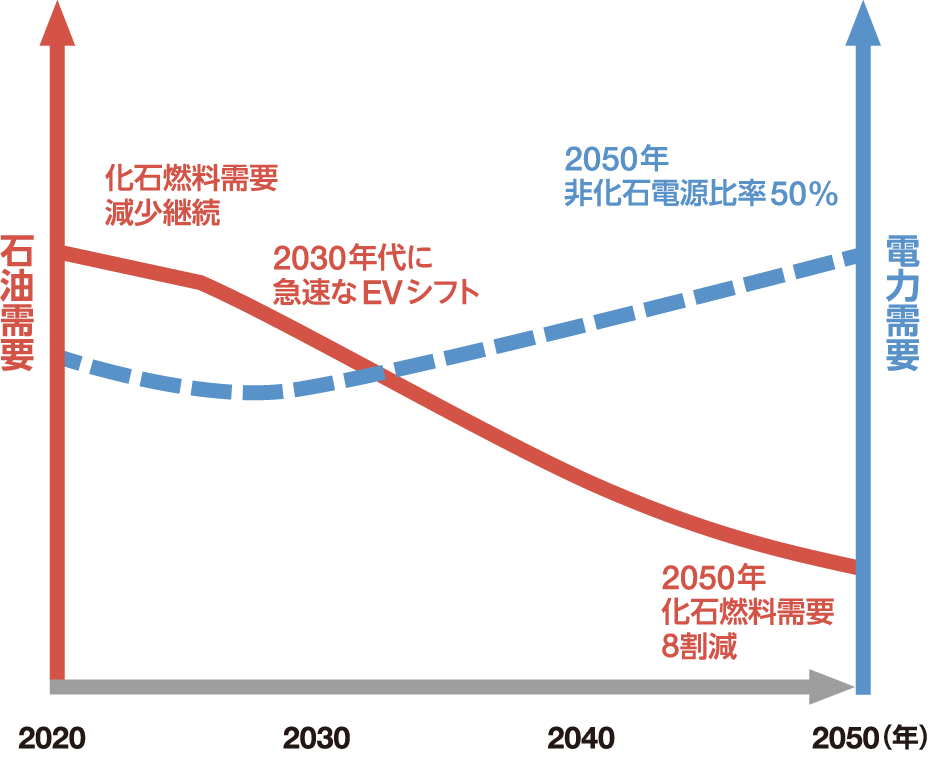
Japan

Asia Pacific

Japan

Asia Pacific

Japan
Risks and opportunities
Based on long-term business environment scenarios for 2050, we are identifying risks and opportunities related to climate change. We have summarized the expected timeline, financial impact level, and our response for each area, and are proceeding with specific initiatives in accordance with the details listed in the table below.
In response to risks and opportunities, we will work to strengthen the profitability of existing businesses and improve capital efficiency, create new businesses through business structure reforms investments, and transform our business portfolio. As a result, as of 2030, we are targeting an operating profit + equity profit/loss base of 270 billion yen.
| Classification | Content | Time axis | Financial impact *1 | Our response | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ~2025 | ~2030 | ~2050 | level 1 |
level 2 |
level 3 |
|||
|
Move line Li vinegar nine Transition risks |
Decrease in domestic fossil fuel demand | ● | ● | ● | ✓ |
|
||
| Decrease in energy and Resources prices due to technological innovation | ● | ● | ✓ |
|
||||
| Full-scale introduction of carbon pricing by the government | ● | ● |
|
|||||
| Regulations on fossil Resources extraction business and cautious investment and lending stance of financial institutions | ● | ● | ✓ |
|
||||
| Declining brand image for companies with high carbon emissions | ● | ● |
|
|||||
|
thing Reason Li vinegar nine Physical risks |
Damage to coastal bases and impact on operations due to natural disasters and sea level rise | ● | ● | ✓ |
|
|||
| Impact on land and sea transportation due to abnormal precipitation and frequent typhoons, etc. | ● | ● |
|
|||||
|
machine Association Opportunities |
Increasing demand for fossil alternative fuels (solid fuels) | ● | ● | ✓ |
|
|||
| Increasing demand for fossil fuels (gaseous fuels) | ● |
|
||||||
| Increasing demand for fossil alternative fuels (liquid fuels) | ● | ● |
|
|||||
| Increasing importance of low-carbon fuel/raw material supply bases | ● | ● |
|
|||||
| Increasing demand for products and materials that contribute to the realization of carbon neutrality society | ● | ● | ✓ |
|
||||
| Growing demand for next-generation storage batteries | ● | ● |
|
|||||
| Full-scale expansion of recycling to realize a recycling-oriented society | ● | ● |
|
|||||
| Stable supply of energy to local communities | ● | ● | ● | ✓ |
|
|||
| Expansion of electric vehicles | ● | ● | ● |
|
||||
| Growing demand for renewable energy | ● | ● | ● |
|
||||
| Evolution of distributed energy systems and growing demand | ● | ● | ● |
|
||||
*1 Financial impact over a long-term timeline Level 1: ~5 billion yen, Level 2: 5 billion yen ~ 50 billion yen, Level 3: ~50 billion yen
*2 Super engineering plastics, oxide semiconductors, high-performance asphalt, environmentally friendly agricultural and livestock materials, etc.
Transition strategy
"Our response" to the above risks and opportunities includes potential themes for provide for society up to 2030. We are working on these as part of our transition strategy towards 2050.
Investment decision-making system
We plan to invest a cumulative 1 trillion yen by 2030 to expand new businesses that contribute to CN.
The provide for society status of each project that contributes to CN may change significantly depending on future trends in technology development and policy trends in each country/region, so we will run various options simultaneously and implement the system shown in the diagram below. During Medium-term Management Plan (FY2023-2025), we will carefully select investment projects through screening based on the social value and investment efficiency of each project.
In addition, investments related to new projects are determined by checking the changes in Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions before and after the project, as well as the reduction contribution of others, and then setting an internal carbon price (internal carbon pricing, 100$/t-CO₂ ) to conduct sensitivity analysis and use it as a reference when evaluating investment projects.
External evaluation of our transition strategy
Our transition strategy has been adopted as a model case for climate transition finance led by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry.
Risk management
Metrics and targets
Concept of setting indicators
In order to realize carbon neutrality society, we will reduce our own direct and indirect emissions (Scope 1, 2) through business operations, and contribute to the reduction of others' emissions through the provision of new products and services (Scope 3 reduction, We believe that efforts from both sides (creating reduction contribution amount) are necessary.
In moving forward with this initiative, we need to consider how we can simultaneously contribute to the environment by reducing emissions, contribute to society by supplying energy, and contribute to the economy by maintaining and expanding corporate profits. Recognizing that it is important to see how well we can achieve our goals, we have set the three indicators listed below to monitor the progress of related activities.
*Indicators 2 and 3 have been revised in light of trends in international discussions regarding avoided emissions.
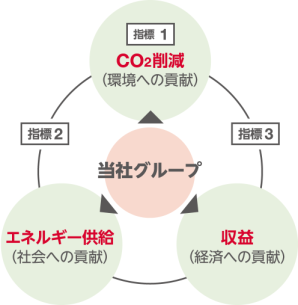


Indicator 1
Scope1+2 emissionsAn indicator that shows how much CO₂ emissions associated with business execution can be suppressed
Indicator 2
Carbon IntensityAn indicator that shows how much low-carbon energy an energy company can supply to society
Indicator 3
Fossil fuel business revenue ratio *2An indicator that shows the extent to which the proportion of fossil fuel business in company-wide profits can be suppressed while maintaining and expanding profits by expanding businesses other than fossil fuels.
Including offset due to negative emissions
*2 Revenue ratio of Petroleum + Resources business to total company revenue (operating + equity profit/loss) [excluding inventory impact]
Target value
The target values (target levels) for each indicator are as described below.
Indicator 1
(Scope1+2 emissions)2030: ▲46% (compared to 2013)
2050: Carbon neutral (CN)
Progress of this indicator value
●CO₂ emissions (Scope1+2)
*Aggregation targets: Idemitsu Kosan, consolidated refining companies (TOA Oil Co., Showa Yokkaichi Sekiyu Co., Seibu Oil Co.), and major consolidated companies
While we promoted energy-saving activities at each Refineries/Complexes, in fiscal 2022, due in part to the impact of economic recovery from the coronavirus pandemic, the operating rate of group Refinery increased by 6% compared to the previous year, and Scope 1+2 emissions decreased. , a slight increase from the previous year.
Indicator 2
(Carbon Intensity)2030: ▲10% (compared to 2020)
2040: ▲50% (compared to 2020)
Regarding reducing emissions throughout the supply chain in order to realize carbon neutrality society, from the perspective of simultaneously contributing to the environment (reducing CO₂ ) and contributing to society (supplying low-carbon energy needed by society), We will set target values using an index called "Intensity" and proceed with related initiatives.
*The area graph in the figure shows the low carbon degree of society based on the IEA scenario (our assumption)
The "Energy one step ahead" that we are promoting as a future business field is an initiative that will greatly contribute to Scope 3 reduction, and we hope to contribute to the realization of carbon neutrality society through provide for society of this field. .
| Provide for society theme | Estimated business scale | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | 2030 | 2040 | |
| Hydrogen/ammonia | Million tons | 100 | 400 |
| SAF/biofuel/ synthetic fuel | Million kL | 50 | 250 |
| Blending non-fossil fuels into gasoline * | % | 10 | 20 |
| Idemitsu Green Energy Pellets | Million tons | 300 | 300~ |
| Afforestation, CCS, etc. | Million tons | 100 | 700 |
* Target in 2030 assumes high-octane gasoline
Indicator 3
(Fossil fuel business revenue ratio)2030: 50% or less
●Image of reducing Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions through business portfolio transformation
Initiatives
Climate change adaptation response
In response to increasingly severe natural disasters, we can anticipate various types of damage such as earthquakes, tsunamis, and storm surges, extract risks, and minimize damage to Refineries / Complexes in the event of a disaster and quickly restore their original condition. Extremely important. We will continue to fulfill our mission of supplying energy by strengthening our hardware by investing in equipment to strengthen our security capabilities, and by enhancing our intangible aspects from the perspective of disaster mitigation in the event of unexpected disasters.
In recent years, more and more typhoons are moving across the country while maintaining their strength, and climate change is said to be a contributing factor. Storm surges brought about by typhoons increase the risk of flooding for Refineries / Complexes located in coastal areas. Therefore, we are simulating the route in which the largest typhoon expected in the future will land directly on Refineries / Complexes, and conducting risk analysis on the impact of flooding from storm surges. Based on the results of this analysis, we are considering hardware reinforcement measures such as installing flood walls in the seawater pump room, as well as soft disaster mitigation measures by enhancing the disaster prevention response manual.
●Estimated typhoon path as a prerequisite for studying storm surge damage estimation Refinery
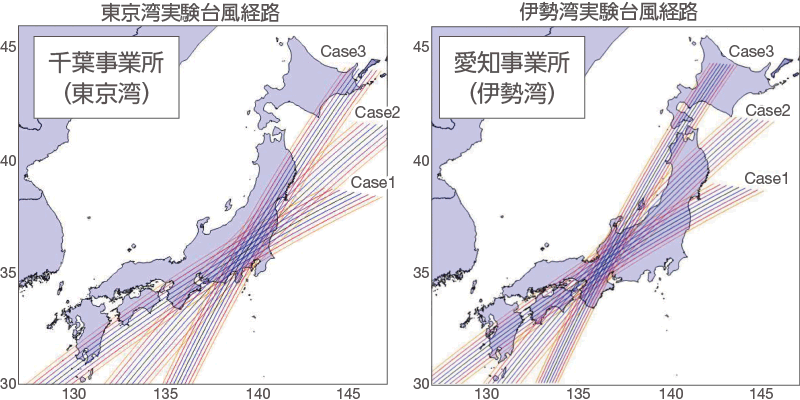


●Estimated image of storm surge damage
Reducing CO₂ emissions throughout the value chain
Low-carbon Petroleum
In order to realize the energy transition, we will first steadily make use of our assets (customers, human resources, stores, systems, infrastructure, equipment, etc.) and, in conjunction with new investments for next-generation businesses, provide diverse services to our customers. We will create a system that can provide a stable supply of energy.
In the biomass fuel field, we have built a SAF manufacturing facility (production capacity: 100,000 kL) at Chiba Complex using cutting-edge technology, and we plan to start supplying it in 2026, contributing as a low-carbon solution for the air transportation industry. We are aiming for This initiative has been selected as a Green Innovation Fund project *1 by NEDO (New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization).
Our interim goal is to build a system to produce 500,000 kL of SAF *2 annually in Japan by 2030. In building this system, we will link raw material procurement and expansion into biochemistry, and will also begin supplying biodiesel, an internal combustion engine oil, to customers.
*2 SAF: Sustainable Aviation Fuel
Jet fuel is produced from sustainable sources with low CO₂ emissions during the process from raw material production and collection to combustion.
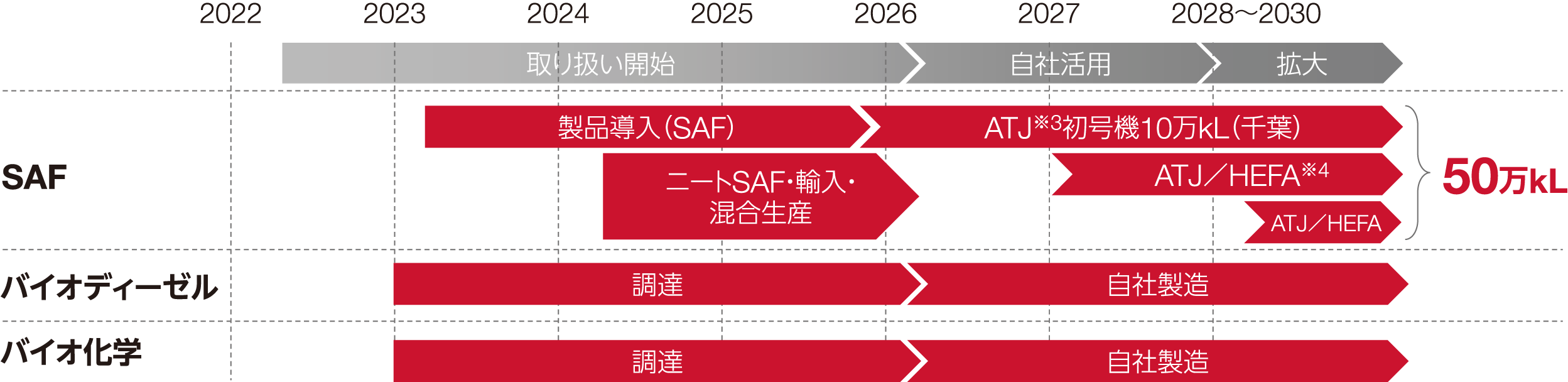





※3 ATJ:Alcohol To Jet
It is a technology and process for producing SAF from ethanol, and has been certified as the international standard "ASTM D7566 Annex 5" for SAF.
※4 Hydroprocessed Esters and Fatty Acids:Hydroprocessed Esters and Fatty Acids
SAF production method for hydrotreating used cooking oil, vegetable oil, etc.
Establishment of CNXcenter concept
Our establishment of CNXcenter concept is to leverage the characteristics and strengths of Refineries/Complexes have operated for many years as fossil-based energy production bases, while reborn as new carbon-neutral fuel and product supply bases. In doing so, we will build a new supply chain according to the characteristics and demands of the industrial complex where each base is located, contributing to the "carbon neutrality" of the industrial complex as a whole.
Building an ammonia supply chain at Tokuyama Complex and Shunan area
Four companies, Tosoh Corporation, Tokuyama Corporation, and Japan Zeon Corporation, have started a joint study with the aim of establishing a supply system for more than 1 million tons of carbon-free fuel ammonia per year at the Shunan Complex by 2030. We will develop our Tokuyama Complex piers and storage facilities as a common supply base for ammonia in the Shunan Complex, and study the ammonia supply infrastructure for the Shunan Complex companies (on the demand side). In addition, based on this project, the four companies will promote the construction of Japan's first ammonia supply chain in the Shunan region through various initiatives, such as demonstrations of ammonia combustion in actual equipment.
SAF manufacturing using ATJ process technology at Chiba Complex
We are working to develop the world's first 100,000 kL class ATJ demonstration facility, and will construct a SAF production equipment using ATJ technology at Chiba Complex in 2025, with supply starting in 2026. Regarding bioethanol, the raw material, we will diversify our procurement from within and outside of Japan, building Japan's first large-scale supply chain, and aim to provide for society as soon as possible. By 2030, we will build an annual production system of 500,000 kL.
Promoting energy conservation and zero emissions of power consumption
Implementation of efficiency improvement work on heavy oil direct desulfurization equipment
In May 2020, we carried out renovation work to improve the efficiency of the heavy oil direct desulfurization equipment (RH equipment) at Chiba Complex. This work is intended to comply with the low sulfur content regulations for marine fuel set by the IMO (International Maritime Organization).
Construction of high-efficiency naphtha cracking furnace (Tokuyama Complex)

A high-efficiency naphtha cracking furnace was newly installed in Tokuyama Complex and commercial operation began in February 2021. The high-efficiency naphtha cracking furnace increases the yield of ethylene and improves thermal efficiency by pyrolyzing naphtha in a short period of time. As a result, it is possible to achieve an energy saving effect of about 30% compared to ethylene production using a conventional cracking furnace, and contributes to a reduction of about 16,000 tons of CO₂ per year. Naphtha is a petroleum product that is pyrolysis via a cracking furnace and becomes the basic raw material for petrochemicals such as ethylene and propylene.
Tokuyama Complex produces approximately 620,000 tons of ethylene annually using ethylene production equipment, mainly supplying it to the Shunan Complex (Shunan City, Yamaguchi Prefecture). This time, two old naphtha cracking furnaces in the ethylene production system were shut down and one high-efficiency naphtha cracking furnace was newly installed.
Expanding the use of electricity derived from renewable energy
Starting in fiscal 2020, we have decided to use CO₂-free electricity (3,732kW of contract power) provided by Idemitsu Green Power oil terminal terminals and other locations in Japan.
Supplying renewable energy to offshore oil fields
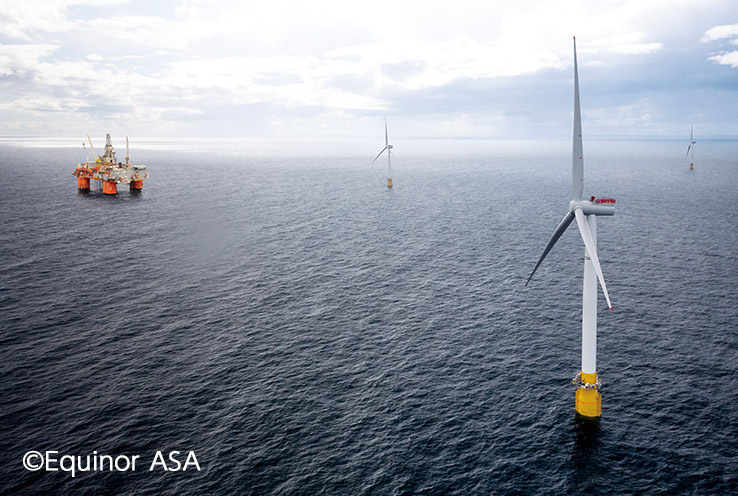

Our equity method affiliate INPEX Norway Co., Ltd., through its Norwegian subsidiary INPEX Idemitsu Norge, submitted to the Norwegian government a development plan to introduce floating offshore wind power generation in the Snorre oil field in which it has an interest, and received approval from the Norwegian government. . In May 2023, we began transmitting electricity to the Snorre oil field using floating offshore wind power generation. This development plan is an offshore wind farm (name: Hywind Tampen floating wind farm) consisting of 11 floating offshore wind power generation facilities with a rating of 8,000 kW (88,000 kW in total) located approximately 200 km off the coast of the city of Bergen in western Norway. This is the world's first attempt to construct a new plant and connect it directly to oil and gas production facilities. Going forward, we will continue to actively incorporate advanced technology and promote the reduction of environmental impact in our Resources business.
Supply of environmentally friendly products and services
Sales of coal boiler control optimization system (ULTY-V plus™)
We jointly developed the boiler control optimization system "ULTY-V plus™" with the NYK Group. By introducing ULTY-V plusTM, coal consumption can be reduced by approximately 1%, resulting in improved economic efficiency for customers and a reduction in CO₂ emissions. In March 2019, we established Yusen Idemitsu Green Solutions Co., Ltd. in a 50-50 partnership with the NYK Group, and are focusing on proposal and sales with this company at the core. In fiscal 2021, we received an order for four units from Hokuriku Electric Power Co., Inc., and the installation of these four units is expected to reduce CO₂ emissions by approximately 100,000 tons per year. We will continue to promote sales domestically and internationally. In addition, we have developed a system (product name: "BAIOMIX™", hereinafter "this system") that calculates the optimal co-combustion rate of biomass fuel in coal boilers, and began sales in August 2021.ULTY -By installing this system into the V plus system, it will be possible to optimally and automatically control biomass co-firing in coal boilers.
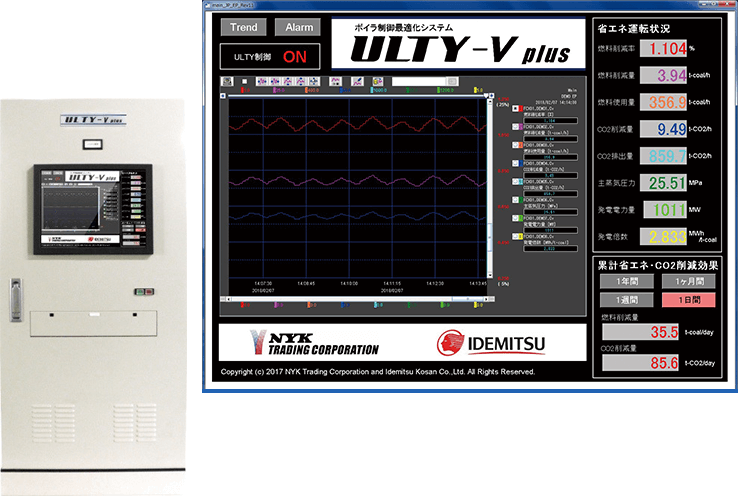
In order to expand biomass co-firing at coal-fired power plants, we have developed torrefied wood pellets, "Idemitsu Green Energy Pellets" which have excellent crushability and calorific value, and can be handled in much the same way as coal. We are working to reduce CO₂ emissions using existing coal-fired power generation equipment.
This newly developed system calculates the impact and economic burden on equipment and power generation efficiency due to biomass co-firing, including Idemitsu Green Energy Pellets, and uses AI (artificial intelligence) to determine the optimal co-firing rate based on past co-firing rate data. Calculate the mixed combustion rate. In addition to the method in which coal and biomass fuel are mixed in existing equipment and then combusted, it can be used in various combustion methods, such as a method in which biomass fuel is input through a dedicated line and co-combusted with coal in the furnace.
Expansion of renewable energy power generation
Tokuyama biomass power generation project initiatives
Our group is engaged in the biomass power generation business as an initiative that contributes to CO₂ reduction through the use of renewable energy and local production and consumption of energy. To date, we have invested in Tosa Green Power Co., Ltd. in Kochi Prefecture and Fukui Green Power Co., Ltd. in Fukui Prefecture, and have developed the Keihin Biomass Power Plant, which utilizes a former Refinery refinery site.
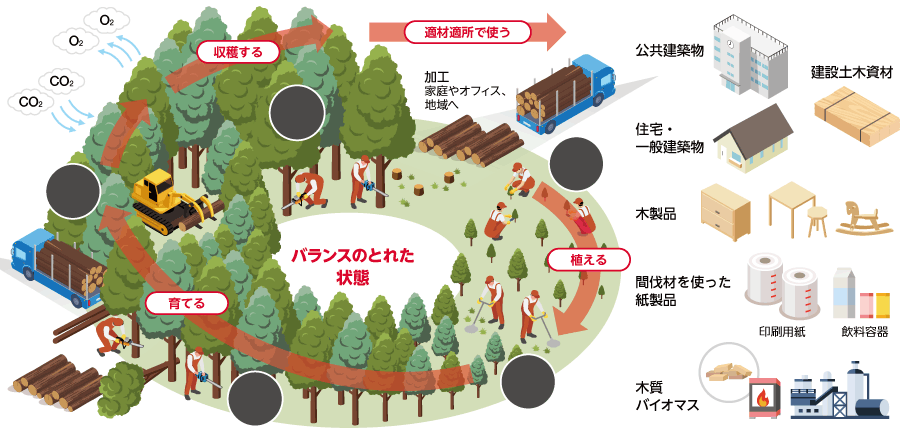
In January 2023, we began commercial operation of the Tokuyama Biomass Power Plant, the group's fourth site. This power plant utilizes part of the site of Refinery (currently Tokuyama Complex), which closed in 2014, and existing infrastructure. Approximately 70% of Japan's land area (37.8 million hectares) is forest, and the utilization of thinned wood that remains unused has been a long-standing issue. For the time being, our company will use imported wood pellets and palm kernel shells (PKS)*, but in the medium to long term, we will use domestically produced thinned wood and sawn wood scraps to create an environment-friendly solution. We will contribute to sustainable forest creation, forestry promotion, and the cyclical use of domestic forest Resources.
In addition, our company has been participating in the Woody Biomass Utilization Promotion Council, which was launched in January 2021 by Shunan City, Yamaguchi Prefecture, since its inception. Taking advantage of the regional characteristics of both abundant forest Resources and biomass power generation facilities, we will work together with local governments to promote the use of domestically produced woody biomass materials, and build and develop a circular economy through local production and local consumption of energy and promotion of forestry. We will continue to contribute to
*Both wood pellets and PKS have obtained third-party certification at the supplier, ensuring sustainability and traceability in production and manufacturing processes, and consideration for the global environment, biodiversity, working environment, etc. Use approved materials.
●Image of cyclical use of forest Resources (created by our company based on the figures published in the Forestry Agency's FY2021 Forest and Forestry White Paper)


Construction of a geothermal power plant in Yuzawa City, Akita Prefecture
As part of our efforts to expand our geothermal business, we are jointly working with INPEX Corporation and TEPCO Renewable Power Co., Ltd. on a plan to install a geothermal power plant (name: Snail Mountain Power Plant, output: 15,000 kW) in Yuzawa City, Akita Prefecture. We have decided to move on to the construction phase. The power plant will be built on Mt Snail and will be operated by Oyasu Geothermal Co., Ltd., a company invested in by three companies, with operation scheduled to begin in March 2027. As a result of the blowout test (demonstration test to evaluate production capacity) conducted in 2021, it is expected that stable production of geothermal fluid (steam and hot water) equivalent to an output of approximately 15,000 kW will be possible in the long term. Yes, the electricity generated is certified under the renewable energy FIT (Fill-in Tariff) system. In addition, the Snail Mountain Power Plant will work to construct and operate power plants that contribute to the local community by designing them with consideration for the environment and landscape. Unlike renewable energies such as solar power generation, geothermal power generation has been attracting increasing attention in recent years as an energy source that can provide a stable power supply regardless of the weather. We will continue to actively promote the spread and expansion of renewable energy, and hope to contribute to Japan's energy security and the realization of a low-carbon society.
Verification of commercialization of pumped storage hydropower generation at the Musselbrook coal mine site

Leveraging its business base in Australia, the company is considering using former mining sites as bases for various renewable energy sources. We have begun a joint feasibility study with Australia's power company AGL Energy for a pumped storage power generation project that will utilize the former site of Australia's Musselbrook Coal Mine, which will be completed in 2022. Australia has favorable climate conditions such as wind and sunlight, and is a large country with abundant renewable energy potential, so the Australian government is promoting an energy transition toward decarbonization. In particular, energy storage through pumped storage power generation is expected to contribute to power system stability and play an essential coordinating role in the transition to renewable energy. We will continue to actively respond to Australia's energy transition and work to create low-carbon and decarbonized businesses.
Expanding supply of biomass fuel
Idemitsu Green Energy Pellets
Coal-fired power generation emits more CO₂ per kWh (amount of electricity generated) than other power sources, so there is a need for solutions to reduce CO₂ emissions. One of these is the use of biomass fuel, which is a carbon-neutral raw material. Biomass fuel is an organic material derived from plants, which absorbs CO₂ through photosynthesis during the growth process of living organisms.
By 2030, we are aiming for annual production of 3 million tons of Idemitsu Green Energy Pellets a biomass solid fuel to replace coal. We will complete construction of a factory in Vietnam in fiscal 2023, and will continue to contribute to carbon neutrality by expanding our production base and production volume.
●Production system roadmap (image)
Collaboration with other companies to expand renewable energy
EV charging service demonstration using dynamic pricing
Our company and Solar Frontier Co., Ltd., together with Nissan Motor Co., Ltd., are working on a demonstration project for an EV charging service that utilizes our unique dynamic pricing *1.
The three companies will work on this demonstration with the aim of reducing and leveling the power load in the future, when electric vehicles such as EV *2 and PHV *3 become more popular. This demonstration will verify the effective use of renewable energy for EV charging and a mechanism that enables charging to avoid times when electricity demand is high, contributing to the achievement of carbon neutrality and the realization of sustainable electricity infrastructure. We aim to do so.
-
Dynamic pricing: A pricing system that fluctuates depending on conditions such as demand and supply.
-
EV: Electric vehicle (driven by electric motor)
-
PHV: Plug-in hybrid vehicle (driven by electric motor and fuel engine)
Development and provide for society of innovative technology
Joint study towards CCUS implementation in Tomakomai area, Hokkaido
Our company, Hokkaido Electric Power Co., Ltd., and Japan Petroleum Resources Co., Ltd. are three companies in the Tomakomai area of Hokkaido that utilize the business bases and strengths of the three companies to develop CCUS (Carbon dioxide Capture, Utilization, and Storage: CO₂ capture and We have started a joint study toward the realization of effective utilization and storage. With a view to launching a CCUS project that connects multiple points in the Tomakomai area by 2030, we are conducting technical studies related to CO₂ emission points, CO₂ recovery equipment, CO₂ transport pipelines, and suitable site surveys for CO₂ storage points. We will proceed with specific investigations and examinations, focusing on the following. In addition to storing CO₂ , we will also take on the challenge of using it as Resources to produce synthetic fuel.