Innovation management (research and development)
Basic approach
Idemitsu Kosan has positioned "contribution to a carbon neutral, circular society" and "contribution to local communities (energy & mobility)" as key challenges, and is developing a strategy that brings together the technologies of the entire company while also utilizing external technologies.
Governance
Our group's research and development system consists of Advanced Technology Research Laboratories and the research laboratories of each division, which are responsible for specialized development. We have also established a company-wide Research & Development Committee that not only considers direction and strategy, but also strengthens cooperation between research laboratories and improves our technological capabilities.
Strategy
We have contributed to society by bringing a wide range of products to the market, which can be said to be the result of our various technological developments.
We will implement measures, including those for our research and development structure, to further promote the organic integration of technologies we have built over the years. Of the three business areas in which we will contribute to provide for society in line with Vision for 2050, research and development will play a particularly important role in realizing "Energy one step ahead" and "Diverse resource conservation / circulation solutions." Furthermore, in our R&D restructuring, we have integrated some of our organizations to establish an Innovation Center ahead of the completion (scheduled for the end of fiscal 2027) of the Integrated Research Laboratory, which we have decided to establish as a base for technology integration. This new organization will restructure its roles and functions for research and development and new business creation, contributing to the acceleration of the transformation of our group's business portfolio. We will continue to strive to achieve sustainable growth, increase our corporate value, and become a business entity that can contribute to society.
● Contributing to provide for society of R&D toward Vision for 2050
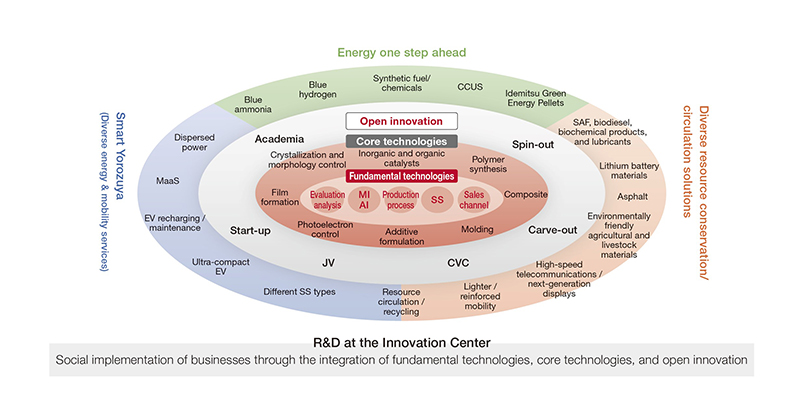


Initiatives
Strengthening the system for creating innovation
In order to build a system that can operate the internal and external co-creation process for provide for society at a higher level, we established the Innovation Center in July 2025, which consists of the Next Generation Research Institute that will promote medium- to long-term research, Innovation Strategy Department that will be responsible for formulating R&D strategies, and the Intellectual Property Department that will handle intellectual property strategies. As the innovation hub for the Group, the new organization will strengthen management in order to steadily engage in R&D even in an uncertain environment.
The Integrated Research Institute (scheduled for completion at the end of fiscal year 2027), which will consolidate the majority of the Group's domestic research functions, will bring together R&D technologies and know-how to accelerate co-creation. It will establish a consistent system from R&D for provide for society to process engineering and commercialization, and maximize the Group's technological capabilities.
Research and development investment results
The Group is engaged in research and development into Petroleum, Functional materials, Resources, and even new business creation. Under the R&D structure, we work closely together to carry out R&D activities.
● Actual R&D investment amount for fiscal 2024 (unit: million yen)
| Research and development expenses | 33,916 | |
|---|---|---|
| Breakdown by segment | Petroleum | 391 |
| Functional Materials | 12,474 | |
| Power/Renewable energy | 139 | |
| Resources | 457 | |
| Others | 20,455 | |
New innovations from CVC
Since 2019, Idemitsu has been accumulating knowledge about startups through investments in venture capital funds in Japan, the United States, and Europe. As the next step, Idemitsu CVC was established in July 2024. Over the three years until 2026, the company has set aside an investment limit of up to 10 billion yen to invest in and collaborate with startups with innovative technologies and business models. At the end of 2024, amid a rapid increase in data traffic volume, as exemplified by the expansion of data centers, and the increasing importance of faster communication speeds, Idemitsu invested in NLM Photonics, a developer of high-speed communication device materials, to gain knowledge about market trends and technological innovations in the next-generation communications field.
Overview of Idemitsu CVC Initiatives
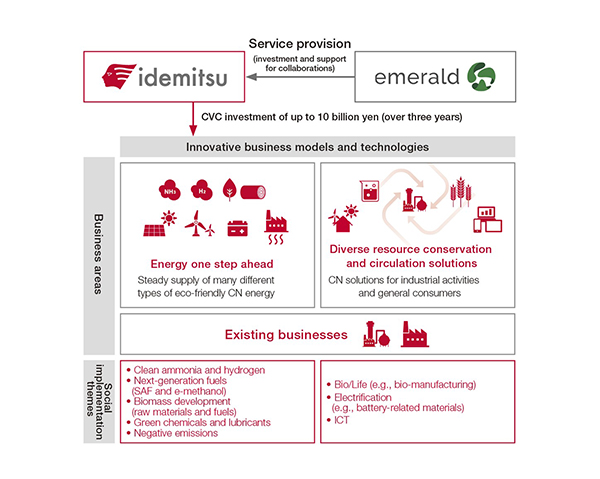


Towards creating new value and business
In the early stages of research and development, such as exploration and research, which are the key to creating new business, we not only engage in cross-internal activities that utilize our own technology and knowledge, but also actively collaborate with outside parties to promote openness. With innovation at the center of our efforts, we are working to accelerate the creation of new businesses to transform our business portfolio.
Theme creation through cross-departmental initiatives
Our activities to create medium- to long-term new business themes (advanced materials project) are in their third year, and we continue to mobilize the wisdom of a total of 30 people. The themes created through these initiatives are not limited to internal consideration, but are also promoted through collaboration with universities and startups to materialize business plans. Through these initiatives, we are also continuing to develop co-creative innovation human resources.
●Activities aimed at creating new business


Academia collaboration
In the early stages of research and development, such as exploration and investigation, which are key to creating new businesses, we are actively working on open innovation by collaborating with external parties.
Through the activities of the "Idemitsu Kosan Next-Generation Materials Creation Collaborative Research Center," which was established at the Tokyo Institute of Technology (now Tokyo University of Science) in fiscal year 2020, we are working with Tokyo University of Science to acquire technologies in key areas in the field of advanced materials and in the field of CNX solutions. We have also established a joint research department with Kobe University and are collaborating with academia, including the University of California, Santa Barbara.
To develop next-generation technologies in the carbon-neutral field, we have concluded a comprehensive collaboration agreement with the University of Tokyo's Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology and the Institute of Industrial Science (2024) and are engaged in joint research.
Promoting MI and DX
We are working to accelerate research and development through MI (Materials Informatics) and strengthen DX promotion.
-
Reskilling: We continue to implement and promote literacy improvement measures across all research laboratories, such as sharing internal initiatives and holding workshops, as well as practical training in the use of data science and generative AI.
-
DX solution development: In collaboration with domestic and international consulting companies, we are promoting the development of solutions to key MI and DX issues in each R&D area, such as the digitalization of analytical technology.
-
Environment development: We are developing a company-wide dedicated data science cloud environment that allows for safe and flexible use of open databases and open source software, which are essential for MI and DX. We are also building RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation), which combines in-house data with generative AI.
New business creation
Development of a greenhouse gas fixation plant using purple photosynthetic bacteria
As a result of our new business creation activities, we began investigating a technology for fixing CO₂ and N₂ using purple photosynthetic bacteria, and are now working to commercialize it in collaboration with Symbiobe, a startup company spun off from Kyoto University.
By combining Symbiobe's photosynthetic microorganism technology with our process technology for scale-up, we aim to provide for society of greenhouse gas fixation such as CO₂ and the production of green biomaterials *.
* Products related to food and the environment that are produced using the metabolic activity of microorganisms
Development of solar cells for space
The space industry market has been expanding rapidly in recent years, and is expected to reach $1 trillion by 2040. We will accelerate our efforts to enter the space industry market by utilizing the CIGS solar cell technology we have cultivated over the years.
Our CIGS solar cells are thin-film, lightweight solar cells composed of Cu (copper), In (indium), Ga (gallium), and Se (selenium). Because they have higher radiation resistance than existing space solar cells, they demonstrate excellent performance over long periods even in the harsh space environment, contributing to the stable operation and long life of spacecraft such as artificial satellites. We are promoting commercialization with the aim of implementing them in a wide range of space applications, from low-orbit satellites to missions in high-radiation environments, and even future lunar exploration. With CIGS solar cells, we will support future space development from an energy perspective.
Idemitsu CIGS solar cell

Idemitsu CIGS solar cell

Idemitsu CIGS solar cell
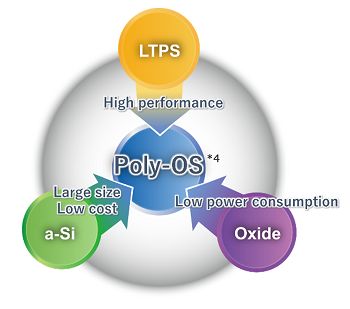
Developing innovative semiconductors that combine high performance, low cost, and low power consumption to meet the demand for lower power consumption caused by advances in high-speed communications and digital technology
In 2006, we started developing the polycrystalline oxide *1 semiconductor material IGO (Indium Gallium Oxide). The IGO we developed is characterized by its high mobility, which is on the same level as low-temperature polysilicon (LTPS) *2, which was not possible with conventional oxide semiconductor materials. In addition, it is suitable for processes in large-scale lines for 8th generation and above, making it possible to manufacture large-area backplanes *3.
Backplanes using IGO combine all the advantages of existing technologies (high performance, low-cost manufacturing, and low power consumption), and are therefore expected to contribute to the evolution of display performance, the development of the display industry, and the realization of a low-carbon society through reduced power consumption for displays.


*1 Polycrystalline oxide: A thin polycrystalline film composed of metal elements and oxygen.
*2 Low-temperature polysilicon (LTPS): Polycrystalline silicon formed on a glass substrate at low temperatures. High electron mobility.
*3 Backplane: A circuit board on which minute semiconductor elements that form the basis of a flat-panel display are mounted.
*4 Poly-OS: Polycrystalline oxide semiconductor