Water Resources
Basic approach
The Idemitsu Group's water risks are managed in group-wide risk management as part of ''risks due to changes in the external environment surrounding our business,'' ''risks due to natural disasters and accidents,'' and ''risks related to climate change and environmental regulations.''
Under the "Environmental Conservation Policy," we set goals and conduct wastewater treatment to meet national and local government standards in order to prevent pollution, use Resources effectively, maintain biodiversity, and other aspects of our environmental management system. We are incorporating it into practice.
Policy
Governance
Strategy
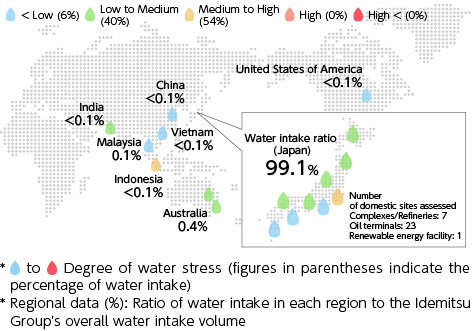
The Group strives to understand water Resources usage on a global scale, and is identifying water-stressed areas of its business sites with reference to Aqueduct information from the World Resources Institute (WRI). None of the Group's domestic sites are located in water-stressed areas, but the combined water withdrawal ratio for the seven Refineries/Complexes accounts for 98% of the Group's total. Therefore, we will thoroughly manage water quality in Japan and work to reduce water usage and use Resources more effectively through the recycling of water Resources.
The Group also operates in countries and regions where water Resources are not necessarily abundant. Water Resources issues around the world are becoming more serious, and it is said that there are situations and regions where safe drinking water cannot be obtained. Recognizing this situation, we have begun initiatives looking overseas and have published water stress maps.
●Water stress map of our group's main business locations
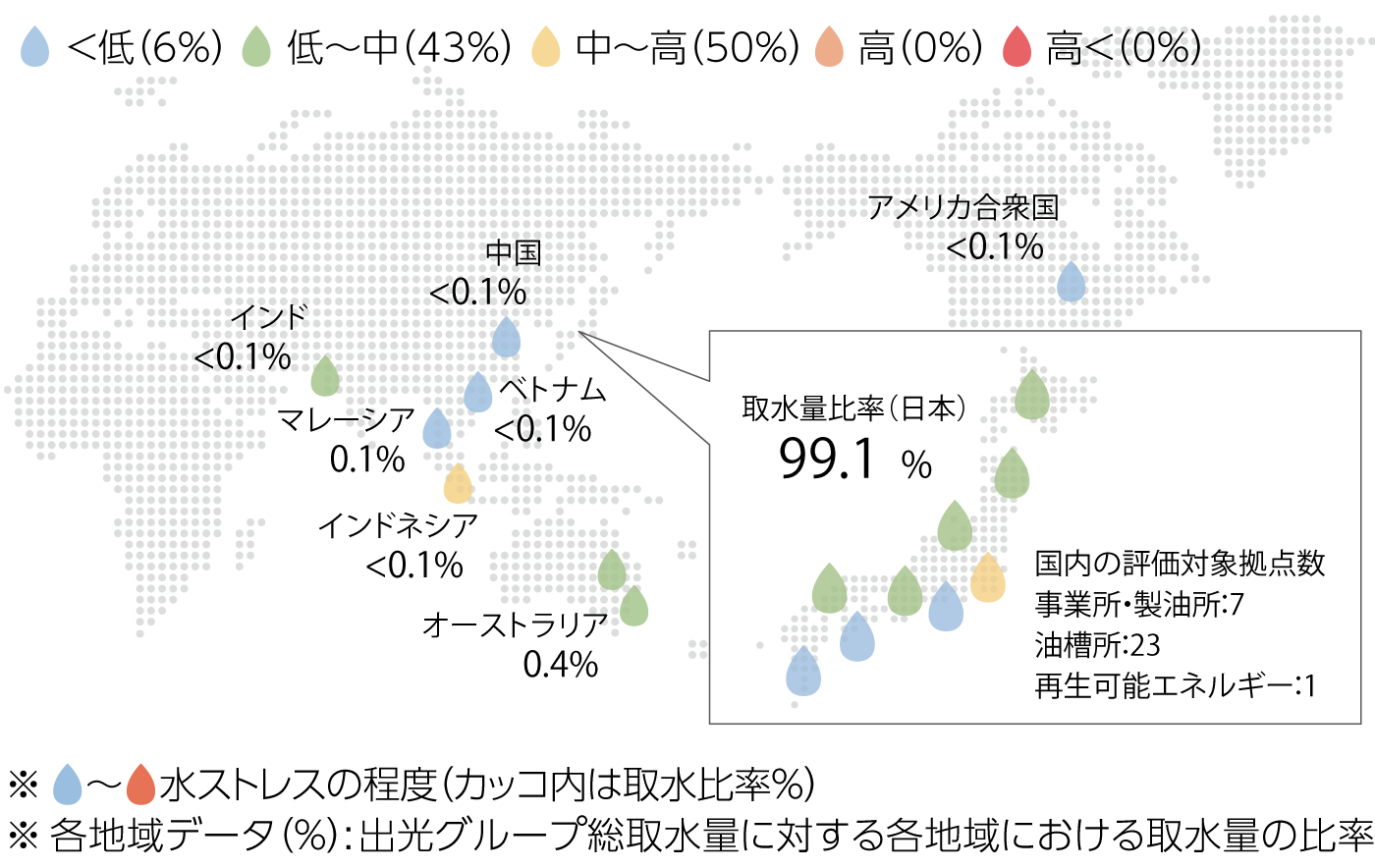
●Major business locations of our group Water Stress Map
Risk management
Initiatives
Strengthening water recycling at Refineries/Complexes
99% of the Group's total water intake comes from Refineries/Complexes. Because Refineries/Complexes use large amounts of water, we are not only complying with wastewater standards but also working to reduce water consumption.
In Refinery petroleum refining process, refineries require a certain amount of water (seawater and freshwater) to cool process fluids. The freshwater (warm water) used for cooling is circulated and cooled in an air-cooled cooler, and is reused as cooling water for process fluids, thereby reducing the burden on the environment. As a water-using business, we will continue to strive to further recycle water Resources. Approximately 94% of the water taken in by Refineries/Complexes is seawater, and approximately 6% is water for industrial use, with the recycling rate of industrial water being 93% in fiscal 2024.
●Industrial water recycling
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
-
Scope of data: Idemitsu Kosan, consolidated refining companies (TOA Oil Co., Showa Yokkaichi Sekiyu Co., Seibu Oil Co.) and major consolidated companies (including Seibu Oil Co. which became a consolidated company in June 2022 and after)
-
The water recycling rate applies only to "industrial water" ((1) Industrial water intake: 94,030,000 tons, (2) Industrial water usage: 1,404,288,000 tons, (3) Industrial water recycled: 1,310,258,000 tons, Water recycling rate = (3)/(2), *(2) = (1) + (3))
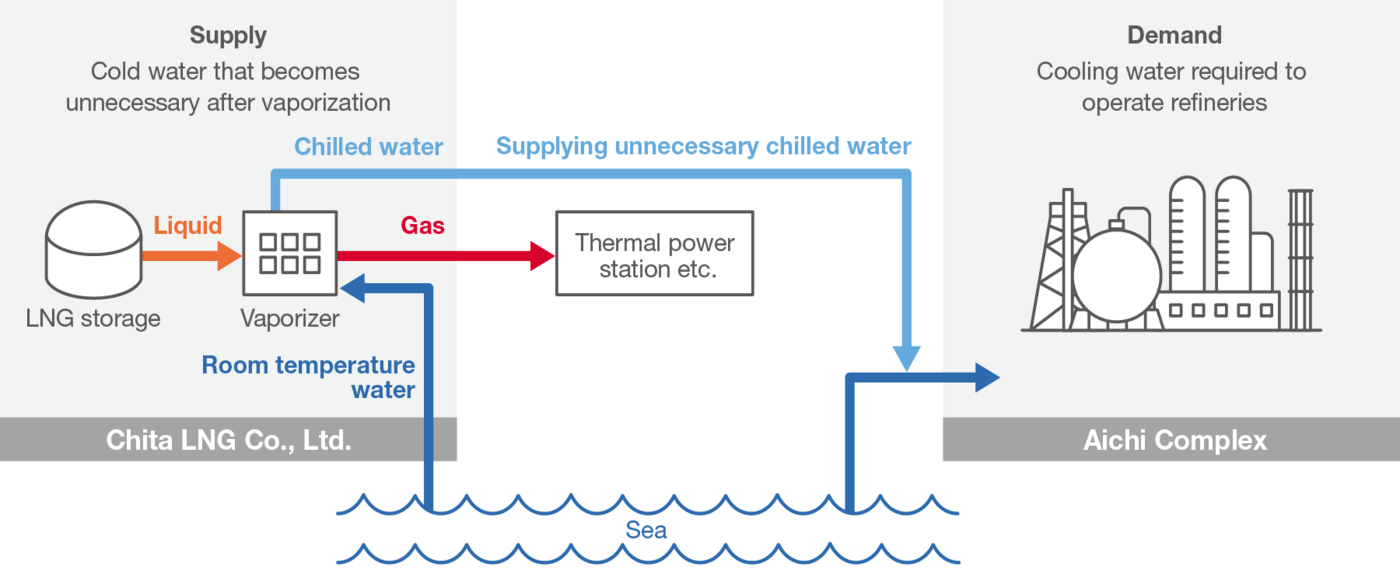
Reducing water usage in collaboration with other companies
At Aichi Complex we share cold water within the petrochemical complex to reduce water usage. By effectively using the cold water discharged from the LNG vaporizers of the neighboring CHITA LNG Co.,Ltd. as process cooling water, we are contributing to a reduction in the amount of water withdrawn throughout the Chita region.
●Cold water distribution through collaboration within the complex


Initiatives for water quality management
When using water Resources, it is also important to manage the quality of water before returning it to the environment. When discharging water, it is treated using multiple facilities to raise the water quality to a level that does not adversely affect the environment, and then returned to the natural environment. As a result of these constant efforts, there were only two violations of laws and regulations regarding wastewater quality management in fiscal 2024, based on the definition of environmental abnormalities *.
-
Environmental anomalies
Cases where the following conditions are not met in accordance with the regulatory standards set forth in environmental laws (including ordinances and agreements):
A. Events deemed necessary under environmental laws and regulations to take "measures in the event of an accident"
B. When an administrative action, guidance, or recommendation is received from an administrative agency and a report or other document for correction is submitted to the administrative agency.
C. When damage to the body, life, property, etc. of neighboring residents is caused by an incident attributable to our company, and compensation is paid.