Waste/ chemical substances/ pollution prevention
Waste reduction
Basic approach
The Group is working to reduce the amount of waste generated and to reuse raw materials and use recycled materials from the perspective of effective Resources utilization, thereby reducing the environmental impact.
Policy
Governance
Strategy
The main waste generated through our business includes waste catalysts from the refining process at Refinery, residues (sludge) from tank cleaning, sludge collected from wastewater treatment facilities, etc. We aim to reduce the amount of this waste and make it harmless through intermediate processing such as incineration, dehydration, and dissolution, and promote recycling as cement raw material, etc., with the aim of achieving "zero emissions" by reducing the amount of final disposal to less than 1%.
Risk management
Initiatives
Reduction targets and results
The petroleum and chemical industries have each set voluntary targets * for reducing the amount of final disposal of industrial waste as part of efforts to create a recycling-oriented society promoted by the Japan Business Federation. Based on these targets, we aim to keep the amount of final disposal of industrial waste at each Refinery and petrochemical plant to 1.0% or less of the amount generated.
*Oil (Petroleum Association of Japan):
<Industry-specific targets> Maintain and continue the zero emissions (final disposal rate of 1% or less) achieved in fiscal year 2020 from fiscal year 2021 onward.
Chemistry (Japan Chemical Industry Association):
<Target for final disposal volume of industrial waste in fiscal 2025> 170,000 tons or less.
<Industry-specific targets>
The final (landfill) disposal volume will be reduced to 170,000 tons or less by fiscal year 2025.
Maintain a Resources rate of 65% or more until fiscal 2025.
Chemical substance management/reduction
Basic approach
As chemical substance management regulations become increasingly strict both in Japan and overseas, the Group is working to manage chemical substances from the following perspectives, based on the "Basic Principles for Quality Assurance" and the "Basic Principles for Safety, Health and the Environment," in order to realize production activities and products that take into consideration the environment and human health.
-
Elimination, substitution, and reduction of hazardous substances based on chemical risk assessment
-
Implementing risk reduction measures when handling chemical substances
-
Improving safety for workers and customers (product users) by obtaining or providing information on chemical substances contained in products
Policy
Governance
Risk management
Initiatives
Management of PRTR substances
Of the substances regulated by the PRTR Law *1 (including HAP *2 and POPs *3), highly volatile substances such as benzene, toluene, xylene, and normal hexane contained in crude oil, petroleum products, and petrochemical raw materials are partially emitted into the atmosphere as VOCs *4 when these substances are received into or discharged from storage tanks, or when products are shipped onto tank trucks or ships. The Group stores these chemical substances in low-volatility floating roof tanks and strives to reduce emissions by recovering VOCs when products are shipped. Chemical substances transferred Complex are also properly disposed of in accordance with the Waste Disposal Law.
*1 PRTR: Pollutant Release and Transfer Register (chemical substance release and transfer amount notification system)
*2 HAP: Hazardous Air Pollutants
*3 POPs: Persistent organic pollutants
*4 VOC: volatile organic compounds Organic Compounds
PCB management
Based on the PCB Special Measures Law and the Basic Plan for PCB Waste Disposal, Refineries/Complexes are taking steps to dispose of oil containing PCBs and equipment that contains them within the designated time periods.
Freon management
The Group is working to prevent the leakage of fluorocarbons. Large process equipment at Refineries/Complexes that uses HCFCs, which have an ozone-depleting effect, is being updated during regular maintenance.
Pollution prevention
Basic approach
To prevent pollution and reduce the burden on the environment, we not only comply with environmental laws but also take voluntary measures in accordance with our company regulations (Basic Guidelines for Safety, Health and the Environment).
Policy
Governance
Risk management
Initiatives
Air pollution prevention
Air pollutants emitted through our group's business include SOx, NOx, soot, and dust emitted from boilers and heating furnaces, and VOCs emitted from crude oil and petroleum product tanks and ship and lorry shipping facilities.For this reason, we manage Refineries/Complexes to comply with emission standards set by laws, regulations, and ordinances, as well as agreed values based on pollution prevention agreements with local governments.
Prevention of water pollution and marine pollution
In offshore oil field development, oily water is generated during exploratory drilling and development. To prevent marine pollution, the generated water is put through a separator, and the oil is transported to land for treatment. The oil-free water is then treated to meet wastewater standards before being returned to the sea. In addition, before exploratory drilling and development, environmental and impact assessments are always carried out by experts to ensure that the environmental impact is at an acceptable level. We also have an "oil spill prevention plan" in place to deal with the unlikely event of an oil spill at sea. In an emergency, we will set up oil fences to prevent the spread of oil and quickly take measures such as recovering any leaked oil.
In order to maintain zero oil spill accidents in ocean-going tanker transport, we are taking measures on both the hard and soft aspects. On the hard side, we are reducing the risk of oil spills by installing double hulls (double-layered outer hull construction to prevent the risk of crude oil spills due to minor damage) on all large tankers currently in operation. On the soft side, we are conducting oil spill prevention training on board and safety and environmental education for all crew members.
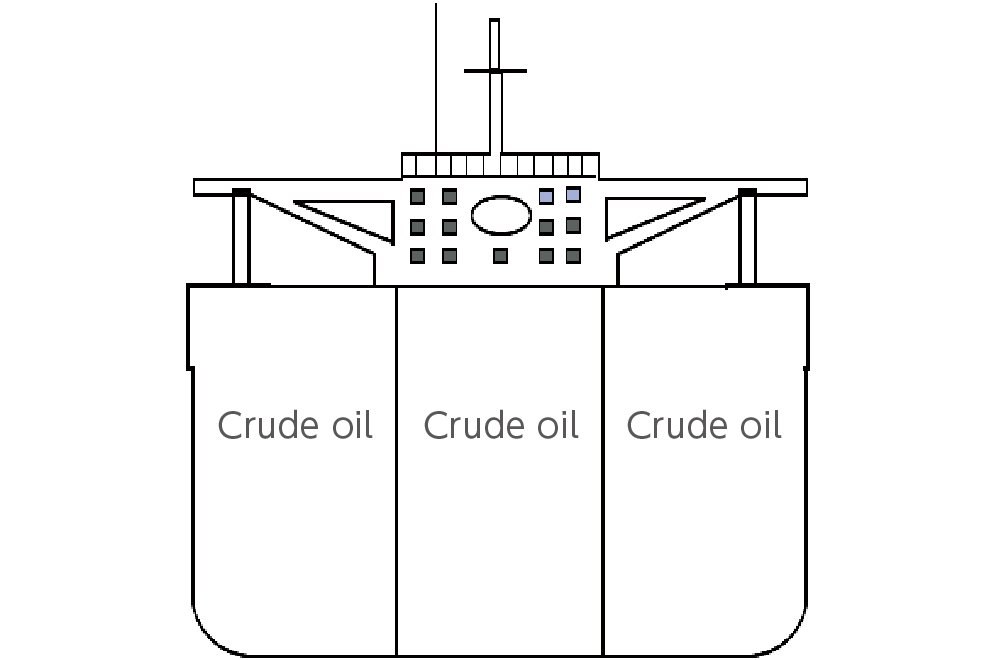
Single hull cross section
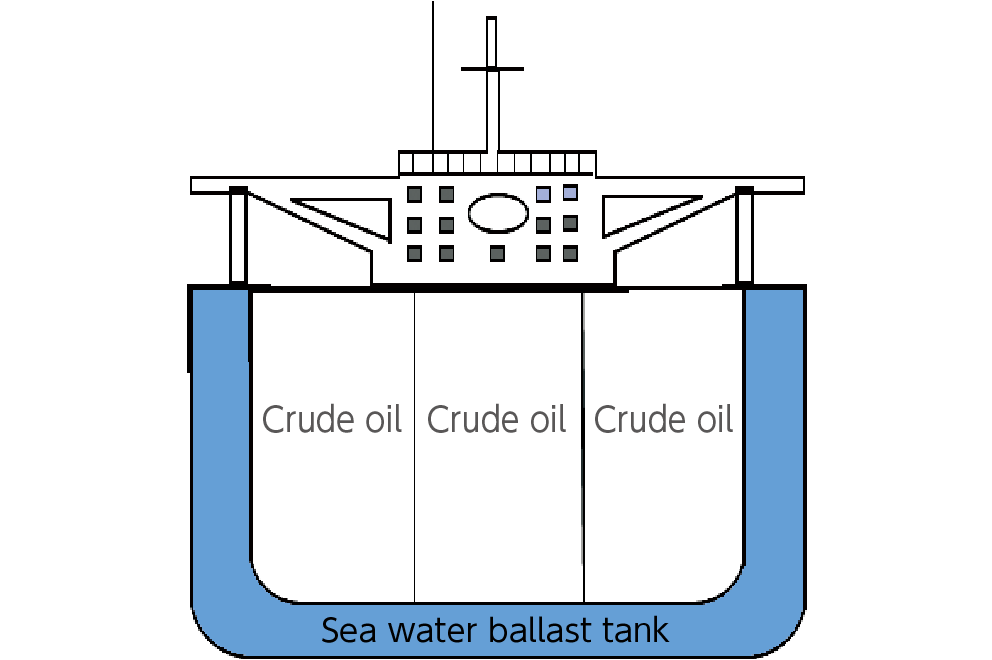
Double hull cross section

Single hull cross section

Double hull cross section

Single hull cross section

Double hull cross section
In addition, our group aims to provide safe and stable energy and materials, and actively engages in environmental conservation activities such as solving the marine plastic waste problem, contributing to the creation of a sustainable society. Masu. Additionally, our group is participating in the Clean Ocean Materials Alliance (CLOMA), which aims to solve the ocean plastic problem.
Soil pollution measures
At Refineries/Complexes, factories, service station, and other facilities that handle petroleum, there is a risk of soil contamination, such as oil leaks from underground pipes. For this reason, our group is working on voluntary investigations of soil and groundwater contamination and purification measures. In particular, when there is a change in the nature of the land, such as the closure or rebuilding of a facility, we work to properly manage the land and prevent contamination from occurring, such as by conducting soil contamination investigations again in accordance with the Soil Contamination Countermeasures Act.