XAREC™ SPS (SPS)
What is the uniquely developed material SPS resin?
SPS (syndiotactic polystyrene) resin is a polymer that Idemitsu Kosan was the first in the world to successfully synthesize in 1985, and our company became the first in the world to commercialize it in 1997.
Because it is lightweight and has excellent heat resistance, hydrolysis resistance, dielectric properties, and chemical resistance, it is used in a wide range of fields, including automobiles, home appliances, and daily necessities.
Idemitsu Kosan offers the brand "XAREC™", a range of grades that use SPS resin.
Features and supply system of SPS resin
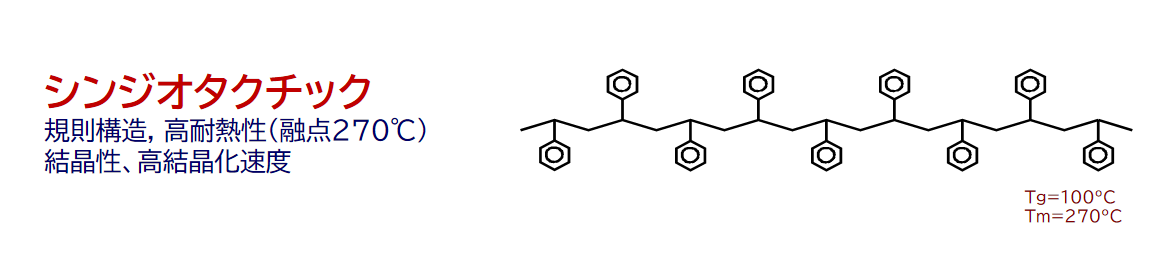
SPS resin is a crystalline, high-performance polystyrene material that inherits the characteristics of polystyrene and has stereoregularity (syndiotactic structure).
It has six characteristics derived from crystallization and polystyrene (non-crystallization).
| Origin | Features | advantage |
|---|---|---|
|
crystallization Features of origin |
Heat-resistant | Melting point 270℃ |
| chemical resistance |
Automotive chemicals/ Detergent resistance |
|
|
polystyrene Features of origin |
Electrical properties Dielectric properties |
Withstand voltage· Suitable for high speed communication |
| Hydrolysis resistance |
in a humid environment Physical property stability |
|
| lightweight | Weight saving | |
|
dimensional stability Liquidity |
low sled Ease of molding |
Positioning of SPS resin in the plastic market
SPS resin is a crystalline resin and is an engineering plastic with a long-term heat resistance of approximately 150℃. Engineering plastic is a general term for plastics with excellent heat resistance and strength. Global demand is said to be approximately 36 million tons/year, and it is mainly used in industrial products.
Crystalline resins generally have high chemical resistance and are hard and rigid, while amorphous resins tend to have high transparency and stable dimensional accuracy.
SPS resin combines the features of crystalline resin and those derived from polystyrene, which is an amorphous resin. It is also a resin that is located between engineering plastics and super engineering plastics (super engineering plastics) with higher heat resistance.
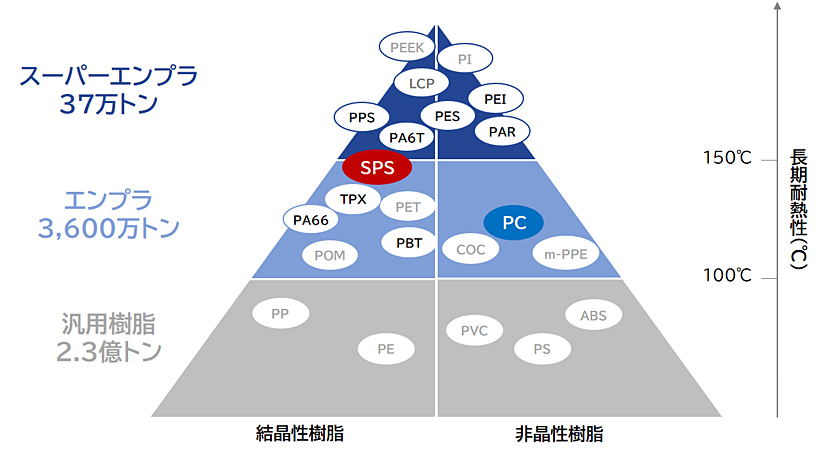
Characteristic comparison with typical engineering plastics
SPS resin is lightweight and has excellent heat resistance, hydrolysis resistance, dielectric properties, and chemical resistance, so it is used in a variety of fields such as automobiles, home appliances, and daily necessities.
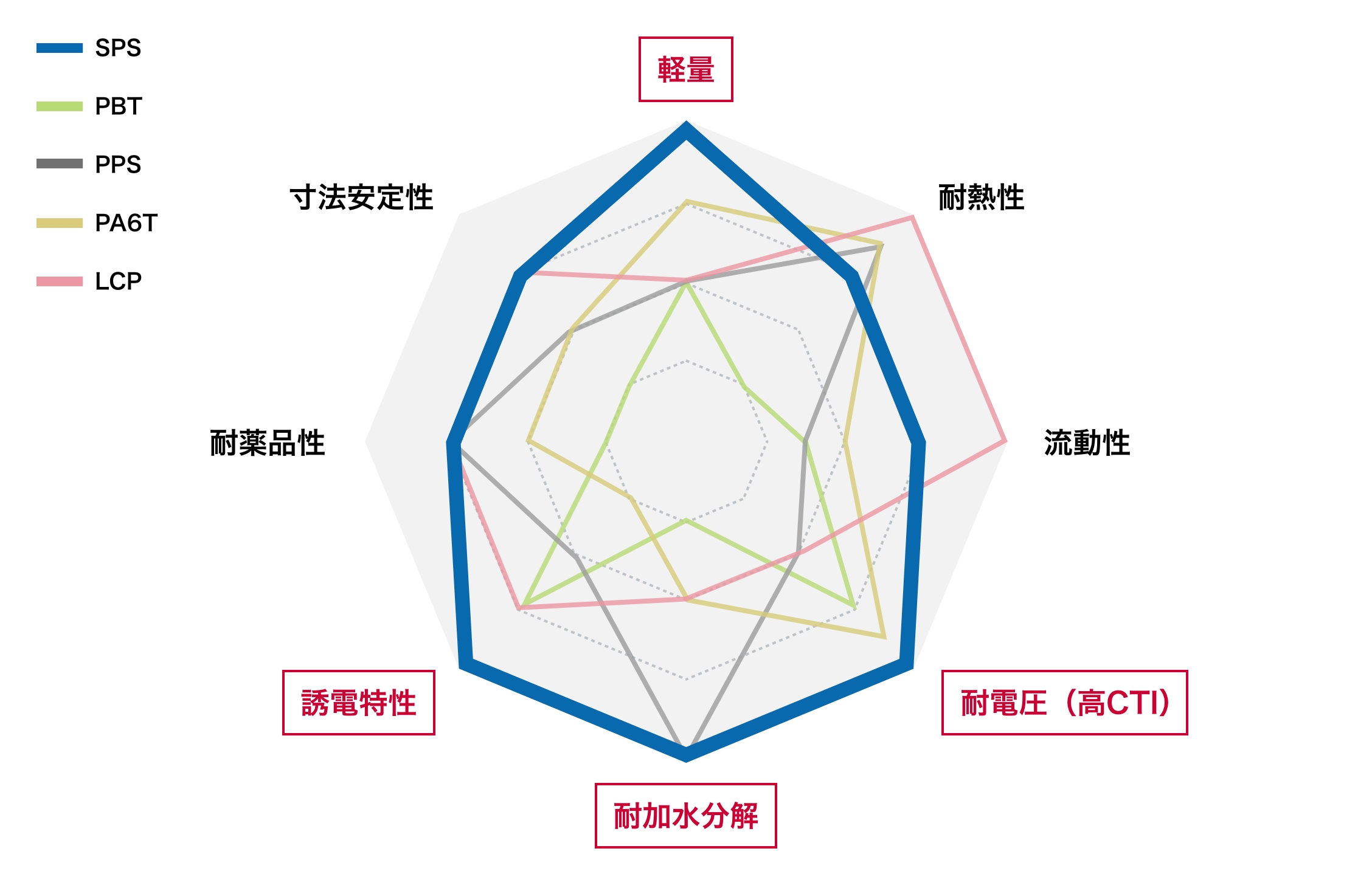
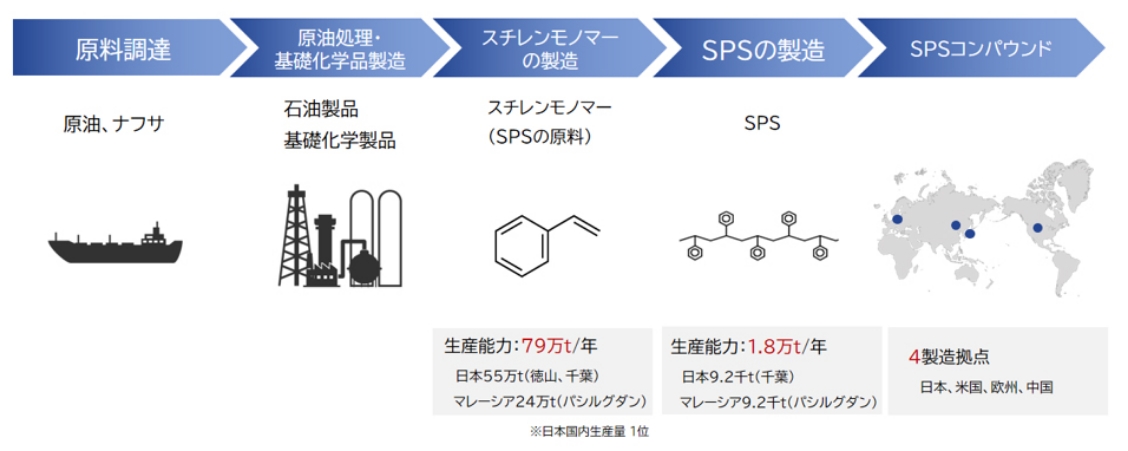
Our company has built an integrated production system, from upstream raw material procurement to SPS resin manufacturing. Compared to engineering plastics, which have a more complex value chain, their strength is that they can be supplied stably.
case study
Automotive applications
We provide various proposals, including improvement measures, and support regarding needs and issues such as vehicle electrification, autonomous driving, safety, and environmental friendliness.

Home appliances/daily necessities
Many resins are used in the fields of home appliances, daily necessities, and housing equipment, and SPS resin is used to improve the functionality of products.

Extrusion/film
SPS resin can be made into fibers and films through extrusion processing. Due to its heat resistance, chemical resistance, and electrical properties, it is increasingly being used in industrial products and daily necessities.

SPS fiber
We are working with textile manufacturers and product manufacturers to develop applications that take advantage of the features of SPS resin.
Regarding fiber applications, we have been conducting joint research with Shinshu University's Faculty of Textile Textiles (Okoshi Laboratory) since fiscal 2012, and we are now on track to improve the physical properties, which had been an issue.
In addition to the potential for producing ultra-fine fibers through composite spinning, we are also investigating processing into knitting, spinning yarn, non-woven fabrics, etc.
SPS biaxially stretched film
SPS resin has unique properties such as hydrolysis resistance, electrical properties, and mold release properties.
By developing applications for high-frequency/high-speed transmission circuit boards, electronic materials, various industrial films, and packaging materials, we will contribute to creating new product value and increasing added value.
Technical data
We have grades available to suit various uses. You can view the main grades and their characteristics, a list of physical properties for each grade, and other technical materials below.
List of major grades
Main features of representative grades for each field
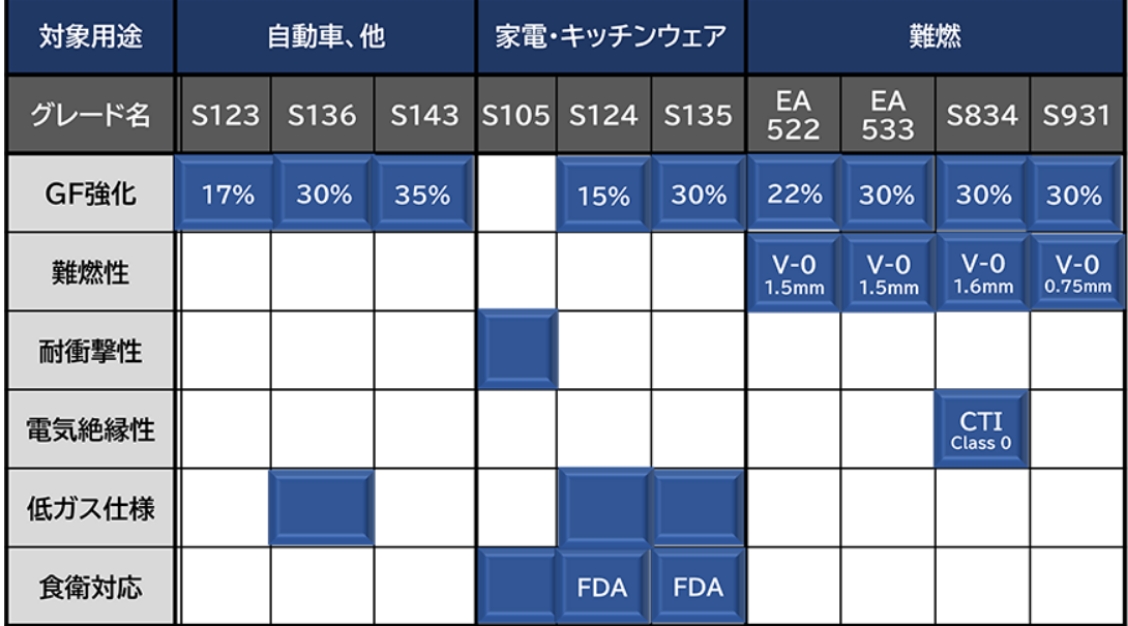
Main grade physical property table
General physical properties table of representative grades for each field
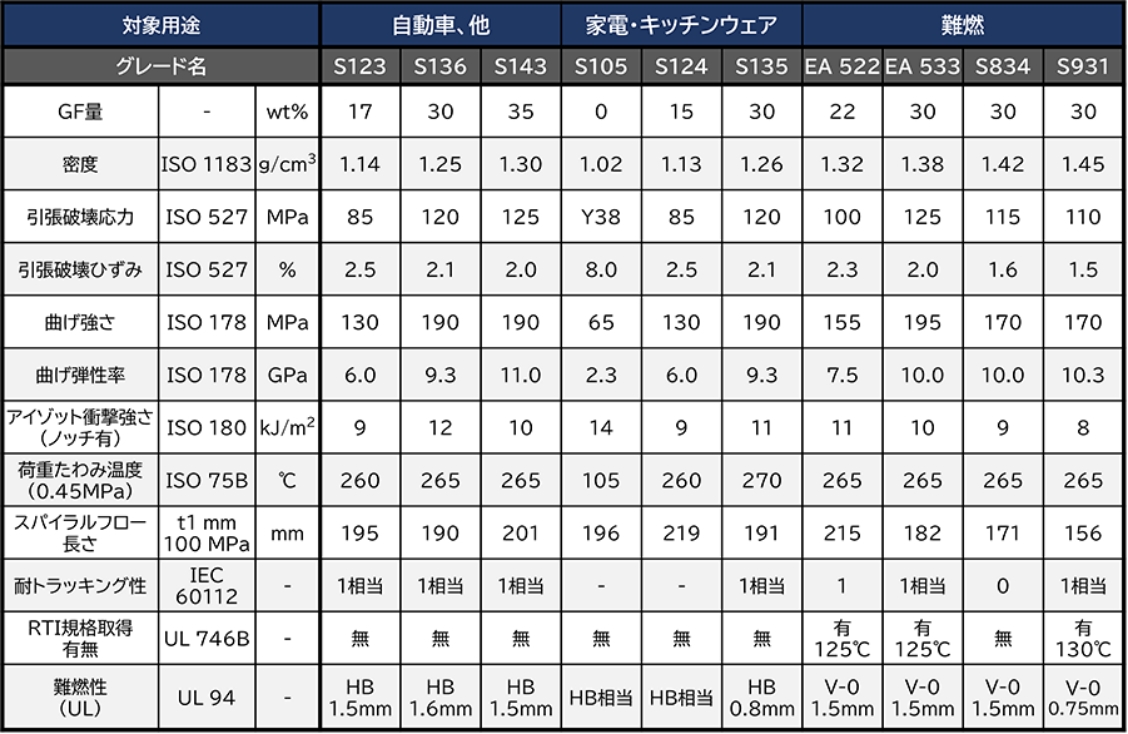
List of other grades
| Grade classification | glass fiber content | grade name |
|---|---|---|
| Glass fiber reinforced, UL94 HB grade | GF15% | C112 |
| GF30% | C132 | |
| GF40% | C142 | |
| GF15% | S124 | |
| GF30% | S135 | |
| GF17% | S123 | |
| GF30% | S131 | |
| GF30% | S136 | |
| GF20% | WA 210 | |
| GF30% | WA 212 | |
| GF40% | WA 214LG | |
| GF30% | WA552 | |
| Glass fiber reinforced, UL94 V-0 grade | GF30% | C832 |
| GF30% | S834 | |
| GF30% | S931 | |
| GF30% | S932 | |
| GF22% | EA522 | |
| GF30% | EA533 | |
| PA66/SPS grade | GF30% | N WA 5030 |
| GF20% | N WA 7020 | |
| GF30% | N WA 7030 | |
| special grade | non-reinforced | SP130 |
| GF15% | SP140 | |
| GF30% | SP151 | |
| non-reinforced | SW130 |
Other technical materials
Various technical documents are available at the SPS special website .